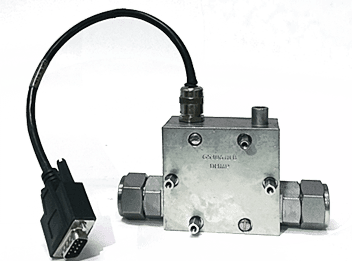
Precision Flow Meters for High Electromagnetic Interference Environments: the Proteus 8000EMR Series
In today’s high-stakes industries, performance isn’t an option—it’s a necessity. From data centers to semiconductor manufacturing facilities, and even military operations, maintaining precise fluid flow is critical. However, high electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI) can disrupt conventional flow meters, leading to unreliable measurement and unplanned operational disruptions. Understanding the Challenge In mission-critical industries […]